CHEMISTRY
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Chapter 1
Chemical Reactions and Equations
● A chemical reaction involves the transformation of one or more substances into
new substances.
● The substances before the reaction are called reactants, and the substances formed
after the reaction are called products.
2. Chemical Equations:
● A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction.
● Reactants are written on the left side, and products are written on the right side of
the arrow.
● Example: 2H2+O2→2H2O
3. Balancing of Chemical Equations:
● The number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the
equation.
● Coefficients are used to balance equations, but subscripts cannot be changed.
● Example: CH4+2O2→CO2+2H2O
4. Types of Chemical Reactions:
● Combination Reactions:
● Two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
● Example: A+B→AB
● Decomposition Reactions:
● A single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
● Example: AB→A+B
● Displacement Reactions:
● One element is replaced by another element in a compound.
● Example: A+BC→AC+B
● Redox Reactions:
● Involves both oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons).
● Example: Zn+2HCl→ZnCl2+H2
● Double Displacement Reactions:
● Exchange of ions between two compounds.
● Example: AB+CD→AD+CB
5. Effects of Chemical Reactions:
● Evolution of Gas:
● Production of gas during a reaction.
● Example: Zn+2HCl→ZnCl2+H2
● Formation of Precipitate:
● Insoluble solid formed during a reaction.
Question 1.
Identify ‘x’, ‘y’ and ‘z’ in the following reaction :![]()
(a) x = gas; y = reaction condition; z = gas
(b) x = solid; y = liquid; z = gas
(c) x = number of moles of KClO3; y = reaction condition; z = number of molecules of oxygen
(d) x = physical state of KClO3 and KCl;
y = reaction condition, z = physical state of O2. (2020)
Answer:![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Following is a balanced chemical equation for the action of steam on iron : 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Reason (R): The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical equation.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. (2020)
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation must obey the law of conservation of mass.
Question 3.
(a) State the law that is followed by balancing a chemical equation.
(b) Balance the following chemical equation: Na + H3O → NaOH + H2 (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Law of conservation of mass is followed for balancing a chemical equation which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. That is, the total mass of the elements present in the products of a chemical reaction has to be equal to the total mass of the elements present in the reactants in a balanced equation.
(b) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Question 4.
Explain the significance of photosynthesis.
Write the balanced chemical equation involved in the process. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Photosynthesis means synthesis with the help of light. It is the process that gives life to all living beings.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants utilize carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen.![]()
Question 5.
Write balanced chemical equations for the following chemical reactions:
(a) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(b) Lead + Copper chloride → Lead chloride + Copper
(c) Zinc oxide + Carbon → Zinc + Carbon monoxide (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(a) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
(b) Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq)+ Cu(s)
(c) ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Question 6.
Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
This reaction can be classified as
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Exothermic reaction
(C) Endothermic reaction
(D) Oxidation reaction
Which of the following is a correct option? (2020)
(a) (A) and (C)
(b) (C) and (D)
(c) (A), (C) and (D)
(d) (A) and (B)
Answer:
(d) The reaction between CaO and H2O to form Ca(OH)2 is an exothermic combination reaction.
Question 7.
When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a (2020)
(a) combination reaction
(b) displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) double displacement reaction.
Answer:
(d) CuSO4 + H2S → CuS + H2SO4
It is a double displacement reaction as in this reaction CuSO4 and H2S reacting by exchange of Cu2+ and H+ ions to from two new compounds i.e., CuS and H2SO4.
Question 8.
In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution :
(A) exchange of atoms takes place
(B) exchange of ions takes place
(C) a precipitate is produced
(D) an insoluble salt is produced
The correct option is (2020)
(a) (B) and (D)
(b) (A) and (C)
(c) only (B)
(d) (B), (C) and (D)
Answer:
(d) In this reaction exchange of Na+ and Ba2+ ions takes place forming BaSO4 which is a white precipitate i.e., an insoluble salt.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 ↓+ 2NaCl
Question 9.
In which of the following, the identity of initial substance remains unchanged? (2020)
(a) Curdling of milk
(b) Formation of crystals by process of crystallisation
(c) Fermentation of grapes
(d) Digestion of food
Answer:
(b): Formation of crystals is a physical change rest others are chemical change.
Question 10.
Study the following equation of a chemical reaction: (Board Term 1, 2015)
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(i) Identify the type of reaction.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation of another example of this type of reaction.
Answer:
(i) Combination reaction.
(ii) Another example of combination reaction is![]()
Question 11.
State the type of chemical reactions, represented by the following equations : (Board Term I, 2014)
(a) A + BC → AC + B
(b) A + B → C
(c) PQ + RS → PS + RQ
(d) A2O3 + 2B → B2O3 + 2A
Answer:
(a) Displacement reaction.
(b) Combination reaction.
(c) Double displacement reaction.
(d) Displacement reaction or redox reaction.
Question 12.
1 g of copper powder was taken in a China dish and heated. What change takes place on heating? When hydrogen gas is passed over this heated substance, a visible change is seen in it. Give the chemical equations of reactions, the name and the colour of the products formed in each case. (2020)
Answer:
When copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance which is copper oxide.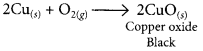
When hydrogen gas is passed over CuO, the black coating on the surface turned reddish brown due to the formation of Cu.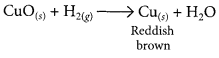
Question 13.
A compound ‘A’ is used in the manufacture of cement. When dissolved in water, it evolves a large amount of heat and forms compound ‘B’.
(i) Identify A and B.
(ii) Write chemical equation for the reaction of A with water.
(iii) List two types of reaction in which this reaction may be classified. (2020)
Answer:
(i) A is calcium oxide, CaO which is used in the manufacturing of cement.
B is calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)3.![]()
(iii) The given reaction is a combination reaction.
Example : NH3(g)(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
2NO(g) + 02(g) → 2NO2(g)
Question 14.
Mention with reason the colour changes observe when:
(i) silver chloride is exposed to sunlight.
(ii) copper powder is strongly heated in the presence of oxygen.
(iii) a piece of zinc is dropped in copper sulphate solution. (2020)
Answer:
(i) When white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight, its colour changes to grey as it decomposes to silver in the presence of sunlight.![]()
This type of reaction is called photodecomposition reaction.
(ii) When copper powder is strongly heated in presence of oxygen, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance which is copper oxide.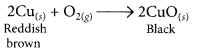
(iii) When a piece of zinc is dropped in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and reddish brown copper metal gets deposited on zinc piece.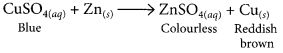
Question 15.
Lead nitrate solution is added to a test tube containing potassium iodide solution.
(a) Write the name and colour of the compound precipitated.
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
(c) Name the type of this reaction justifying your answer. (2020)
Answer:
(a) When lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide then yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed along with potassium nitrate.
(b) Balanced chemical reaction is as follows :![]()
(c) This type of reaction is called precipitation reaction in which one of the products formed is an insoluble substance or this is also called double displacement reaction.
Question 16.
2 g of silver chloride is taken in a China dish and the China dish is placed in sunlight for sometime. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Refer to answer 14(i).
Question 17.
Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(a) It is a displacement reaction.![]()
(b) Refer to answer 15.
Question 18.
2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube. (Al 2019, Board Term 1, 2017, 2016)
(a) List any two observations.
(b) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(c) Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the products formed.
Answer:
(a) Ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO4.7H2O) lose water when heated and the colour of the crystals changes. It then decomposes to ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3) with a smell of burning sulphur.
(b) This is a thermal decomposition reaction.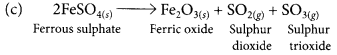
Question 19.
You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance. (AI 2019)
(a) Why has this black substance formed?
(b) What is the black substance?
(c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
(d) How can the black coating on the surface be turned reddish brown?
Answer:
(a) The black substance is formed because copper combines with oxygen.
(b) The black substance is copper oxide (CuO).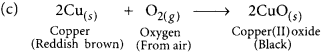
(d) The black coating on the surface can be turned reddish brown by passing hydrogen gas over the hot copper oxide.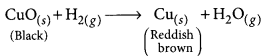
Question 20.
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity. (2018)
Answer:
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of heat:![]()
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of light:![]()
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of electrical energy:![]()
Question 21.
Take 3 g of barium hydroxide in a test tube, now add about 2 g of ammonium chloride and mix the contents with the help of a glass rod. Now touch the test tube from outside.
(i) What do you feel on touching the test tube?
(ii) State the inference about the type of reaction occurred.
(iii) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(i) When barium hydroxide is added into ammonium chloride, the bottom of test tube is found to be cooler.
(ii) It is an endothermic reaction.
(iii) Ba(OH)2 + 2NH4Cl → BaCl2 + 2NH4OH
Question 22.
(a) A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of the chemical reaction.
(b) Ferrous sulphate when heated, decomposes with the evolution of a gas having a characteristic odour of burning sulphur. Write the chemical reaction involved and identify the type of reaction. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(a)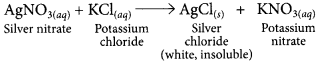
It is a double displacement reaction.
(b) Refer to answer 18(b) and (c).
Question 23.
Name the type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation: (Board Term I, 2016)
(i) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4![]()
Answer:
(i) Combination reaction.
(ii) Precipitation reaction or double displacement reaction.
(iii) Thermal decomposition reaction.
Question 24.
What is a reduction reaction?
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions. (Board Term I, 2015)
(a) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(b) 2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2
Answer:
Those reactions in which addition of hydrogen to a substance or removal of oxygen from a substance take place are called reduction reactions.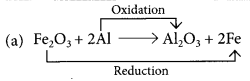
Fe2O3 is getting reduced to Fe and Al is getting oxidised to Al2O3.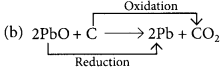
PbO is reduced to Pb and C is oxidised to CO2.
Question 25.
(a) Can a displacement reaction be a redox reaction? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Write the type of chemical reaction in the following:
(i) Reaction between an acid and a base
(ii) Rusting of iron. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(a) Consider the following displacement reaction:
Zn(s)+ CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Here, Zn has changed into ZnSO4 (i.e., Zn2+ ions) by loss of electrons. Hence, Zn has been oxidised. CuSO4 (i.e., Cu2+) has changed into Cu by gain of electrons. Hence, CuSO4 has been reduced. Thus, the above reaction is a displacement reaction as well as a redox reaction.
(b) (i) Neutralisation reaction
(ii) Oxidation reaction.
Question 26.
Mention the type of chemical reaction that takes place when: (Board Term I, 2013)
(i) a magnesium ribbon is burnt in air.
(ii) limestone is heated.
(iii) silver bromide is exposed to sunlight.
(iv) electricity is passed through acidified water.
(v) ammonia and hydrogen chloride are mixed with each other.
Write the chemical equation for each reaction.
Answer:![]()
This is a combination reaction.
This is a thermal decomposition reaction.
This is a photo decomposition reaction.![]()
This is electrolytic decomposition reaction.![]()
This is a combination reaction.
Question 27.
What happens when food materials containing fats and oils are left for a long time? List two observable changes and suggest three ways by which this phenomenon can be prevented. (2020)
Answer:
Food materials containing fats and oils change their taste and smell due to a process called rancidity. Rancidity is a process in which air reacts with fats and oils which changes the smell and taste of food.
Methods of prevention:
Vacuum packing,
refrigeration of food materials,
placing of food materials, away from direct sunlight.
Question 28.
(i) Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction?
(ii) Write chemical name and the formula of the brown gas produced during thermal decomposition of lead nitrate.
(iii) Why do chips manufactures flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen? (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
(i) The glucose produced in our body during digestion combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides energy. The special name of this reaction is respiration. Thus respiration is an exothermic process because energy is produced during this process.
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + Energy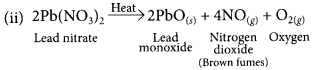
Brown gas evolved is nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
(iii) Chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen because atmospheric oxygen can react with chips which may cause change in colour, change in taste. So to cut the contact between air and the chips, nitrogen gas is used which do prevent its oxidation.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2015
29.“We need to balance a skeltal chemical equation.” Give reason to justify the statement.
Answer:
Skeltal chemical equation are unbalanced. We need to balance chemical equation because of law of conservation of mass. It states that ‘matter can neither be created nor be destroyed’. Therefore chemical equation must be balanced in each and every chemical reaction.
CBSE Class 10 Science – More Resources
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science | NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science |
| CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers | Class 10 Science Important Questions |
30. Name the reducing agent in the following reaction:
3MnO2 + 4Al———— > 3Mn + 2Al2O3
State which is more reactive, Mn or A1 and why?
Answer. ‘Al’ is reducing agent.
‘AT is more reactive than Mn v ‘Al’ displaces Mn from its oxide.
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2015
31.A Name the type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation: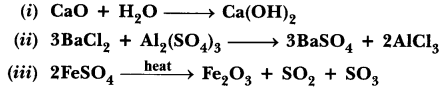
Answer.
(i) Combination reaction
(ii) Double displacement reaction (Precipitation reaction)
(iii) Decomposition reaction.
32. Write the chemical equation of the reaction in which the following changes have taken place with an example of each:
(i) Change in colour
(ii) Change in temperature
(iii) Formation of precipitate
Answer.
(i)Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq)———–> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag
The solution will become blue in colour and shiny silver metal will be deposited.
(ii) NaOH + HCl ———–> NaCl + H2O+ heat
The temperature will increase because heat will be evolved.
(iii) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq)———–> Pbl2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Yellow ppt
Yellow precipitate of Pbl2will be formed.
33.State the type of chemical reactions and chemical equations that take place in the following:
(i) Magnesium wire is burnt in air.
(ii) Electric current is passed through water.
(iii) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases’are mixed.
Answer.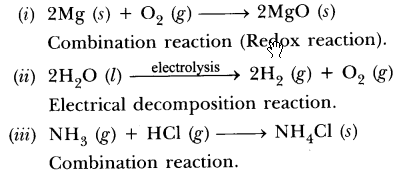
34. 2g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube.
(i) List any two observations.
(ii) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(iii) ‘Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer.
(i) •Green colour of Fe SO4 disappears and reddish brown solid is formed.
• Smell of burning sulphur.
(ii) Decomposition reaction![]()
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2015
35. (a) Define a balanced chemical equation. Why should an equation be balanced?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
(i) Phosphorus burns in presence of chlorine to form phosphorus penta chloride.
(ii) Burning of natural gas.
(iii) The process of respiration.
Answer.
(a) Balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. According to law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(b)(i) P4 (s) + 10Cl2 (g) ———> 4PCl5 (S)
(i)CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) ———> CO2 (g) + 2H2O(l) + heat energy
(iii) C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) + 6H2O ———> 6CO2 (aq) + 12H2O (l) + energy
36.(a) Explain two ways by which food industries prevent rancidity.
(b) Discuss the importance of decomposition reaction in metal industry with three points.
Answer.
(a) (i) Rancidity can be prevented by adding antioxidants to food containing
fat and oil, e.g. butylated hydroxy anisole is added to butter as antioxidant.
(ii) It can be prevented by packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas.
(b) (i) Molten NaCl is electrolytically decomposed to form sodium metal.
(ii) Aluminium metal is obtained by electric decomposition of bauxite ore mixed with cryolite.
(iii) Carbonate ores are thermally decomposed to give metal oxide which on reduction give metal.
Short Answer Type Question[I] [2 Marks] -Year 2014
37. What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate? Name the type of reaction. Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above chemical reaction.
Answer.Yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed. It is precipitation reaction.
Pb( NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) —-> Pbl2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
It is also called double displacement reaction.
short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2014
38.Write chemical equation reactions taking place when carried out with the help of
(a) Iron reacts with steam
(b) Magnesium reacts with dil HCl
(c) Copper is heated in air.
Answer.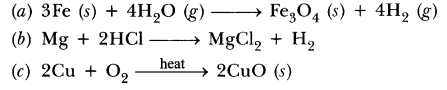
Long Answer Type Question [5 Marks] -Year 2014
39.(a) Write one example for each of decomposion reaction carried out with help of
(i) Electricity (ii) Heat (iii) Light
(b) Which of the following statements is correct and why copper can displace silver from silver nitrate and silver can displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
Answer.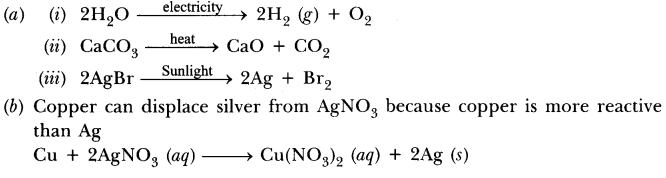
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2013
40. What is meant by skeltal type chemical equation? What does it represent? Using the equation for electrolytic decomposition of water, differentiate between a skeltal chemical equation and a balanced chemical equation.
Answer. The equations in which gaseous are written in atomic form instead of molecular form and equation is not balanced, are called skeltal type equation. They represent gaseous elements formed in atomic state and equation is not balanced
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks]-Year 2012
41.Identify the type of reaction(s) in the following equations.
(i)CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2 H2O
(ii) Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI ——–>Pbl2 + 2KNOs
(iii) CaO + H2O ——–> Ca(OH)2
(iv) CuSO4 + Zn ——–> ZnSO4 + Cu
Answer.
(i) Combustion reaction and oxidation reaction.
(ii)Double displacement reaction and precipitation reaction.
(iii) Combination reaction.
(iv) Displacement reaction.
42.What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
Answer.The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green. The colour changes to reddish brown on heating due to formation of iron (III) oxide.
Give an example each for thermal decomposition and photochemical decomposition reactions. Write relevant balanced chemical equations also.
Thermal decomposition reaction: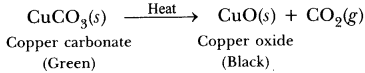
Photochemical decomposition reaction:![]()
43. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it? Write two observations.
Answer. It is because displacement reaction takes place.
Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution and forms pale green
coloured solution of FeS04 and reddish brown copper metal gets deposited.
Fe(s) + CuS04(aq) ——–> FeS04(aq) + Cu(s)
44. Translate the following statement into chemical equation and then balance it Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate. State the two types in which this reaction can be classified.
Answer. 3BaCl2(aq) + A12(S04)3(aq) ——–> 3BaS04(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
It can be classified as double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.
45. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer. In decomposition reaction, a compound is broken down into simpler compounds or elements, e.g.![]()
Combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more elements or compounds combine to form a new compound, e.g.![]()
Thus, decomposition and combination reactions are opposite to each other.
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2012
46. What is rancidity? Mention any two ways by which rancidity can be prevented.
Answer. The process in which taste and smell of food gets spoiled is called rancidity. It happens due to oxidation.
Prevention from rancidity:
(i) Antioxidants are added to fatty acids to prevent oxidation, e.g. chips are packed in presence of nitrogen gas which prevents spoilage by oxidation.
(ii)Food should be kept in airtight container in refrigerator.
47.Write balanced chemical equation for the reactions that take place during respiration. Identify the type of combination reaction that takes place during this process and justify the name. Give one more example of this type of reaction.
Answer. CgH1206 + 6O2 —————> 6CO2 + 6H20 + heat
It is an exothermic combination reaction because heat is evolved.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) ————–>CO2 (g) + 2H20
Combustion of methane is another example of exothermic combination reaction.
48. What is redox reaction? Identify the substance oxidised and the substance reduced in the following reactions.
(i)2PbO + C —–> 2Pb + CO2
(ii)MnO2 + 4HCl —–> MnCl2 + 2H20 + Cl2
Answer. Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously are called redox reactions.
(i) PbO is getting reduced and C is getting oxidised.
(ii) MnOs is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2011
49.State one basic difference between a physical change and a chemical change.
Answer. In physical change, no new substance is formed, whereas in a chemical change, new substance(s) is/are formed.
50. What is meant by a chemical reaction?
Answer. The reaction representing a chemical change is called a chemical reaction.
35.AgN03(aq) + NaCl(aq)——————– > AgCl(s)4↓ + NaN03(aq)
FeS + H2S04————- > FeS04 + H2S↑
Consider the above mentioned two chemical equations with two different kinds of arrows (↑and ↓) along with product. What do these two different arrows indicate?
Ans,↑shows the gas is evolved whereas ↓shows insoluble substance (precipitate) is formed.
51. Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water which is a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why?
Answer. It is because properties of compound (H2O) are different from properties of its constituting elements, i.e. H2and O2.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2011
52.Using a suitable chemical equation, justify that some chemical reactions are determined by:
(i) change in colour, (ii) change in temperature.
Answer.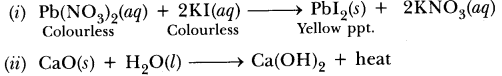
53.(a) A solution of substance ‘X’ is used for white washing. What is the substance ‘X’? State the chemical reaction of ‘X’ with water.
(b) Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer.
(a) ‘X’ is calcium oxide (CaO).
CaO(s) + H2O(l) —–> Ca(OH)2(aq) + heat
(a) It is because iron displaces copper from CuS04 to form FeS04 which is pale green.
Fe(s) + CUS04 (aq)—–> FeS04(aq) + Cu(s)
Blue Pale green
54.Write the balanced equation for the. following reaction and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(i) Potassium bromide + Barium iodide—-> Potassium iodide + Barium bromide.
(ii) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g)—-> Hydrogen chloride(g)
Answer.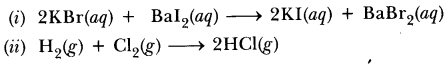
55. A zinc plate was put into a solution of copper sulphate kept in a glass container. It was found that blue colour of the solution gets fader and fader with the passage of time. After few days, when zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of holes were observed on it.
(i) State the reason for changes observed on the zinc plate.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer.
(i) It is because zinc has displaced copper from CuS04. Zinc metal has been used to form zinc sulphate, therefore, number of holes were observed.![]()
56. A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and a residue is left behind.
(i) Name the salt.
(ii) Write the equation for the decom-position reaction.
Answer.
(i) Lead nitrate is white salt.![]()
57. When a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate in a test tube, a reaction takes place.
(a) What type of reaction is this?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
Answer.
(a) Double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.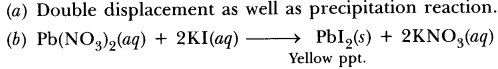
58. Write balanced equations for the following mentioning the type of reaction involved.
(i) Aluminium + Bromine —–> Aluminium bromide
(ii) Calcium carbonate—–> Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide
(iii) Silver chloride—–>Silver + Chlorine
Answer.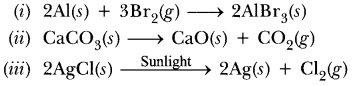
59.(a) Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction?
(b) Define the terms oxidation and reduction.
(c) Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the following reaction.![]()
Answer. (a) It is because heat is evolved during respiration.
(b) Oxidation is a process in which O2 is added or H2 is removed or loss of electrons take place. Reduction is a process in which H2 is added or O2. is removed or gain of electrons take place.
(c) Zn is getting oxidised, CuO is getting reduced.
60.You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black colour substance.
(i) How has this black coloured substance formed?
(ii) What is that black substance?
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
Answer.
(i) Copper reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide which is black, i.e. oxidation of copper takes place.
(ii)Copper oxide![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2010
61. What happens chemically when quicklime is added to water filled in a bucket?
Answer. Quicklime reacts with water to form slaked lime and produces lot of heat and hissing sound.
62. On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
Answer. A chemical reaction is balanced on the basis of law of conservation of mass.
63. What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight? State the type of chemical reaction in this change.
Answer. Silver chloride becomes grey. It is a photochemical decomposition reaction.
64. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium chloride
and silver nitrate indicating the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Answer.![]()
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks]
65. What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction.
Answer. White precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
If both reactants are in solid state, then the reaction will not take place between them.![]()
It is a double displacement as well as a precipitation reaction.
66. What is a redox reaction? When a magnesium ribbon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised or reduced? Why?
Answer. The reactions in which oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons) take place simultaneously are called redox reactions.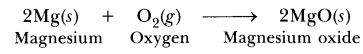
Magnesium is getting oxidised because it is losing electrons to form Mg2+ and oxygen is gaining electrons to form O2-, therefore it is getting reduced.
67. Write any two observations in an activity which may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give an example in support of your answer.
Answer. Any two of these observations will suggest chemical reaction has taken place.
(i) Change in state.
(ii)Change in colour.
(iii) Evolution of gas.
(iv)Change in temperature.
For example, lead nitrate is white crystalline solid which on heating gives yellowish brown solid (lead monoxide). A brown gas and a colourless gas is also evolved. It shows chemical reaction has taken place.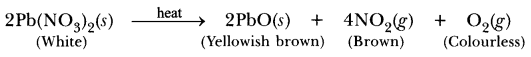
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2009
68.In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
Answer.It is because water contains hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2 : 1.
69.Balance the following chemical equations.
Answer.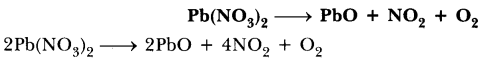
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2009
70. Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
Answer.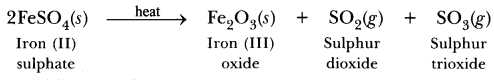
It is decomposition reaction.
71. What is an oxidation reaction? Give an example of oxidation reaction. Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction?
Answer. The reaction in which oxygen or electronegative element is added or hydrogen or electropositive element is removed or loss of electrons takes place, is called an oxidation reaction, e.g. ,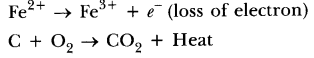
Oxidation reactions are mostly exothermic in nature because heat is evolved in this process.
72. Describe an activity to demonstrate the change that takes place when white silver chloride is kept in sunlight. State the type of chemical reaction which takes place.
Answer.
Aim: To demonstrate the change that takes place when white silver chloride is kept in sunlight.
Materials Required: AgNO3(aq), NaCl(aq), test tubes.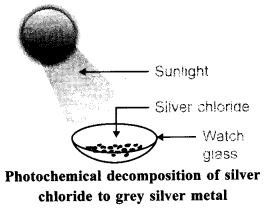
Procedure:
1. Take 5 ml of silver nitrate solution in a test tube.
2. Prepare sodium chloride solution in another test tube.
3. Add sodium chloride solution into test tube containing silver nitrate solution.
4. Observe the colour of silver chloride formed chloride to grey silver metal Dry it with the help of filter papers and place it on the watch glass.
5. Place the watch glass under sunlight for sometime.
6. Observe the colour of the silver chloride after sometime. Observation: White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because silver metal is formed.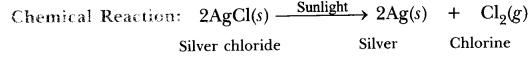
Explanation: Silver chloride is photosensitive. It decomposes in presence of sunlight to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
Conclusion: Decomposition of silver chloride in presence of sunlight is photochemical decomposition reaction.
73.When magnesium ribbon burns in air or oxygen, a product is formed. State the type of chemical reaction and name the product formed in the reaction. Write balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Answer.
![]()
The type of reaction is combination reaction and the product formed is magnesium oxide.
74.Distinguish between a displacement reaction and a double displacement reaction. Identify the displacement and the double displacement reaction from the following reactions.
Answer.
Displacement reaction is a reaction in which more reactive metal can displace less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Double displacement reaction are those reactions in which compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds (?) Double displacement reaction (ii) Displacement reaction
75.When you have mixed the solutions of lead(II) nitrate and potassium iodide,
(i) what was the colour of the precipitate formed and can you name the precipitate?
(ii) write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(iii) is this also a double displacement reaction?
Answer.
(i) The colour of the precipitate is yellow. The name of compound formed as a precipitate is Pbl2 (lead iodide).![]()
(iii) Yes, it is also a double displacement reaction.
CHAPTER 2
ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS
- Definition: Substances that release hydrogen ions () in water; they can also be defined as proton donors.
- Properties: Sour taste, turn blue litmus red, conduct electricity, and react with metals to produce salts and hydrogen gas.
- Examples: Hydrochloric acid (), Sulfuric acid (), Nitric acid ().
- Definition: Substances that release hydroxide ions () in water; they can also be defined as proton acceptors.
- Properties: Bitter taste, feel soapy, turn red litmus blue, and react with non-metallic oxides to produce salt and water.
- Examples: Sodium hydroxide (), Potassium hydroxide (), Calcium hydroxide ().
- Definition: Compounds formed from the reaction between an acid and a base.
- Properties: They are ionic compounds, and their aqueous solutions have no effect on litmus paper.
- Examples: Sodium chloride (), Potassium nitrate ().
Indicators: Indicators are substances which indicate the acidic or basic nature of the solution by the colour change.
Types of Indicator: There are many types of indicators. Some common types of indicators are:
1. Natural Indicators: Indicators obtained from natural sources are called Natural Indicators. Litmus, turmeric, red cabbage, China rose, etc., are some common natural indicators used widely to show the acidic or basic character of substances.
Litmus: Litmus is obtained from lichens. The solution of litmus is purple in colour. Litmus paper comes in two colours- blue and red.
An acid turns blue litmus paper red.
A base turns red litmus paper blue.
Turmeric: Turmeric is another natural indicator. Turmeric is yellow in colour. Turmeric solution or paper turns reddish brown with base. Turmeric does not change colour with acid.
Red Cabbage: The juice of red cabbage is originally purple in colour. Juice of red cabbage turns reddish with acid and turns greenish with base.
2. Olfactory Indicator: Substances which change their smell when mixed with acid or base are known as Olfactory Indicators. For example; Onion, vanilla etc.
Onion: Paste or juice of onion loses its smell when added with base. It does not change its smell with acid
Vanilla: The smell of vanilla vanishes with base, but its smell does not vanish with an acid.
3. Synthetic Indicator: Indicators that are synthesized in the laboratory are known as Synthetic Indicators. For example; Phenolphthalein, methyl orange, etc.
Phenolphthalein is a colourless liquid. It remains colourless with acid but turns into pink with a base.
Methyl orange is originally orange in colour. It turns into the red with acid and turns into yellow with base.
Chemical Properties of Acid:
(i) Reaction of acids with metal: Acids give hydrogen gas along with respective salt when they react with a metal.
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Examples:
Hydrogen gas and zinc chloride are formed when hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc metal.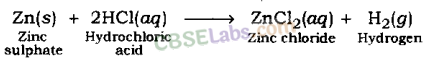
Hydrogen gas and sodium sulphate are formed when sulphuric acid reacts with sodium metal.
Test For Hydrogen Gas: The gas evolved after reaction of acid with metal can be tested by bringing a lighted candle near it. If the gas bums with a pop sound, then it confirms the evolution of hydrogen gas. Burning with pop sound is the characteristic test for hydrogen gas.
(ii) Reaction of acids with metal carbonate: Acids give carbon dioxide gas and respective salts along with water when they react with metal carbonates.
Metal carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Examples:
Hydrochloric acid gives carbon dioxide gas, sodium chloride along with water when reacts with sodium carbonate.
Sulphuric acid gives calcium sulphate, carbon dioxide gas, calcium sulphate and water when it reacts with calcium carbonate
Nitric acid gives sodium nitrate, water and carbon dioxide gas when it reacts with sodium carbonate.
(iii) Reaction of acid with hydrogen carbonates (bicarbonates): Acids give carbon dioxide gas, respective salt and water when they react with metal hydrogen carbonate.
Acid + Metal hydrogen carbonate → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Test For Evolution of Carbon Dioxide Gas: Carbon dioxide turns lime water milky when passed through it. This is the characteristic test for carbon dioxide gas.
The gas evolved because of reaction of the acid with metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate turns lime water milky. This shows that the gas is carbon dioxide gas. This happens because of the formation of a white precipitate of calcium carbonate.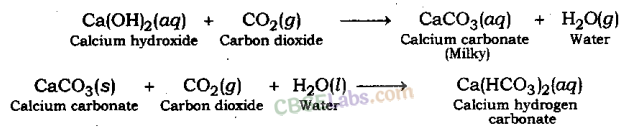
But when excess of carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it makes milky colour of lime water disappear. This happens because of formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate.
Chemical properties of bases:
(i) Reaction of Base with Metals: When alkali (base) reacts with metal, it produces salt and hydrogen gas.
Alkali + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Examples: Sodium hydroxide gives hydrogen gas and sodium zincate when reacts with zinc metal.
Sodium aluminate and hydrogen gas are formed when sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium metal.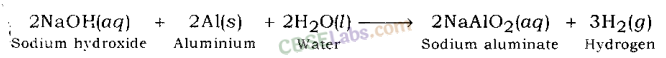
(ii) Reaction of Base with Oxides of Non-metals: Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature. For example; carbon dioxide is a non-metal oxide. When carbon dioxide is dissolved in water it produces carbonic acid.
Therefore, when a base reacts with non-metal oxide, both neutralize each other resulting respective salt and water.
Base + Non-metal oxide → Salt + Water
(Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature)
Examples:
Sodium hydroxide gives sodium carbonate and water when it reacts with carbon dioxide.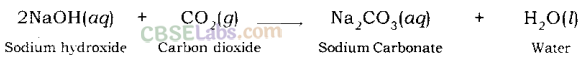
Calcium hydroxide gives calcium carbonate and water when it reacts with carbon dioxide.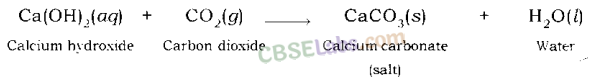
(iii) Neutralisation Reaction: An acid neutralizes a base when they react with each other and respective salt and water are formed.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Since, the reaction between acid and base both neutralize each other, hence, it is also known as Neutralization Reaction.
Examples: Sodium chloride and water are formed when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (a strong base).
In a similar way, calcium chloride is formed along with water when hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide (a base).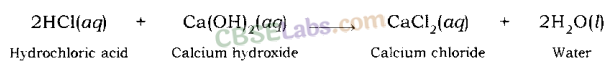
(iv) Reaction of Acid with Metal Oxides: Metal oxides are basic in nature. Thus, when an acid reacts with a metal oxide both neutralize each other. In this reaction, the respective salt and water are formed.
Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water
(Metal oxides are basic in nature)
Examples:
Calcium is a metal, thus, calcium oxide is a metallic oxide which is basic in nature. When an acid, such as hydrochloric acid, reacts with calcium oxide, neutralization reaction takes place and calcium chloride, along with water is formed.
Similarly, when sulphuric acid reacts with zinc oxide, zinc sulphate and water are formed.
Neutralisation Reaction: When an acid reacts with a base, the hydrogen ion of acid combines with the hydroxide ion of base and forms water. As these ions combine together and form water instead of remaining free, thus, both neutralize each other.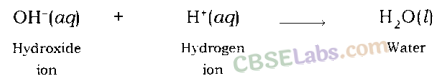
Example: When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide breaks into a sodium ion and hydroxide ion and hydrochloric acid breaks into hydrogen ion and chloride ion.
Hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion combine together and form water, while sodium ion and chloride ion combine together and form sodium chloride.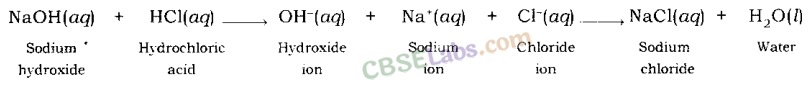
Dilution of Acid and Base: The concentration of hydrogen ion in an acid and hydroxide ion in a base, per unit volume, shows the concentration of acid or base.
By mixing of acid to water, the concentration of hydrogen ion per unit volume decreases. Similarly, by addition of base to water, the concentration of hydroxide ion per unit volume decreases. This process of addition of acid or base to water is called Dilution and the acid or base is called Diluted.
The dilution of acid or base is exothermic. Thus, acid or base is always added to water and water is never added to acid or base. If water is added to a concentrated acid or base, a lot of heat is generated, which may cause splashing out of acid or base and may cause severe damage as concentrated acid and base are highly corrosive.
Strength of Acid and Base: Acids in which complete dissociation of hydrogen ion takes place are called Strong Acids. Similarly, bases in which complete dissociation of hydroxide ion takes place are called Strong Bases.
In mineral acid, such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, etc. hydrogen ion dissociates completely and hence, they are considered as strong acids. Since inorganic acids hydrogen ions do not dissociate completely, so they are weak acids.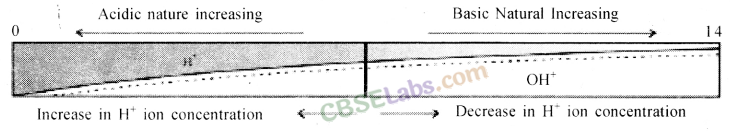
pH value shown by different colours role of pH everyday life:
(i) pH in our digestive system: Dilute HCl (Hydrochloric acid) helps in digestion of food (proteins) in our stomach. Excess acid in stomach causes acidity (indigestion). Antacids like magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] also known as milk of magnesia and sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) are used to neutralize excess acid.
(ii) Tooth decay caused by acids: The bacteria present in our mouth converts the sugar into acids. When the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5, tooth-decaying starts. The excess acid has to be removed by cleaning the teeth with a good quality toothpaste because these kinds of toothpaste are alkaline in nature.
(iii) Soil of pH and plant growth: Most of the plants have a healthy growth when the soil has a specific pH (close to 7) range which should be neither alkaline nor highly acidic. Therefore,
- Compound ‘X’ is Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Compound ‘A’ is Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4).
- Compound ‘B’ is Sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Compound ‘C’ is Sodium acetate (CH3COONa)
Salts: Salts are the ionic compounds which are produced after the neutralization reaction between acid and base. Salts are electrically neutral. There are number of salts but sodium chloride is the most common among them. Sodium chloride is also known as table salt or common salt. Sodium chloride is used to enhance the taste of food.
Characteristics of salt:
- Most of the salts are crystalline soild.
- Salts may be transparent or opaque.
- Most of the salts are soluble in water.
- Solution of the salts conducts electricity in their molten state also.
- The salt may be salty, sour, sweet, bitter and umami (savoury).
- Neutral salts are odourless.
- Salts can be colourless or coloured.
Family of Salt: Salts having common acidic or basic radicals are said to belong to the same family.
Example:
(i) Sodium chloride (NaCl) and Calcium chloride (CaCl2) belongs to chloride family.
(ii) Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Calcium sulphate (CaSO4) belongs to calcium family.
(iii) Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) belongs to the zinc family.
Neutral, Acidic and Basic Salts:
(i) Neutral Salt: Salts produced because of reaction between a strong acid and strong base are neutral in nature. The pH value of such salts is equal to 7, i.e. neutral.
Example : Sodium chloride, Sodium sulphate. Postassium chloride, etc.
Sodium chloride (NaCl): It is formed after the reaction between hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and sodium hydroxide (a strong base).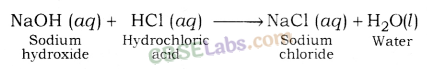
Sodium Sulphate (Na2SO4): It is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and sulphuric acid ( a strong acid).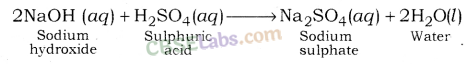
Potassium Chloride (KCl): It is formed after the reaction between potassium hydroxide (a strong base) and hydrochloric acid (a strong acid).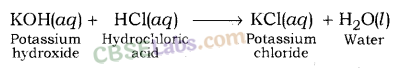
(ii) Acidic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a strong acid and weak base are called Acidic salts. The pH value of acidic salt is lower than 7. For example Ammonium sulphate, Ammonium chloride, etc.
Ammonium chloride is formed after reaction between hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and ammonium hydroxide (a weak base).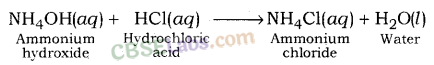
Ammonium sulphate is formed after reaction between ammonium hydroxide (a weak base) and sulphuric acid (a strong acid).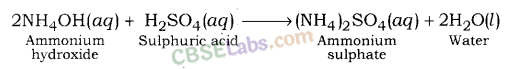
(iii) Basic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a weak acid and strong base are called Basic Salts. For example; Sodium carbonate, Sodium acetate, etc.
Sodium carbonate is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and carbonic acid (a weak acid).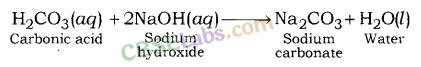
Sodium acetate is formed after the reaction between a strong base, sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and acetic acid, (a weak acid).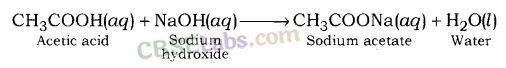
Cause of formation of acidic, basic and neutral salts:
- When a strong acid reacts with a weak base, the base is unable to fully neutralize the acid. Due to this, an acidic salt is formed.
- When a strong base reacts with a weak acid, the acid is unable to fully neutralize the base. Due to this, a basic salt is formed.
- When equally strong acid and a base react, they fully neutralize each other. Due to this, a neutral salt is formed.
pH value of salt:
- Neutral salt: The pH value of a neutral salt is almost equal to 7.
- Acidic salt: The pH value of an acidic salt is less than 7.
- Basic salt: The pH value of a basic salt is more than 7.
Some Important Chemical Compounds
1. Common Salt (Sodium Chloride): Sodium chloride (NaCl) is also known as Common or Table Salt. It is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. It is a neutral salt. The pH value of sodium chloride is about 7. Sodium chloride is used to enhance the taste of food. Sodium chloride is used in the manufacturing of many chemicals.
Important chemical from sodium chloride
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. It is also known as caustic soda. It is obtained by the electrolytic decomposition of solution of sodium chloride (brine). In the process of electrolytic decomposition of brine (aqueous solution of sodium chloride), brine decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. In this process, chlorine is obtained at anode and hydrogen gas is obtained at cathode as by products. This whole process is known as Chlor – Alkali process.
Use of products after the electrolysis of brine:
- Hydrogen gas is used as fuel, margarine, in making of ammonia for fertilizer, etc.
- Chlorine gas is used in water treatment, manufacturing of PVC, disinfectants, CFC, pesticides. It is also used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder and hydrochloric acid.
- Sodium hydroxide is used for degreasing of metals, manufacturing of paper, soap, detergents, artificial fibres, bleach, etc.
2. Bleaching Powder (CaOCl2): Bleaching powder is also known as chloride of lime. It is a solid and yellowish white in colour. Bleaching powder can be easily identified by the strong smell of chlorine.
When calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) reacts with chlorine, it gives calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) and water is formed.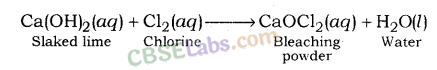
Aqueous solution of bleaching powder is basic in nature. The term bleach means removal of colour. Bleaching powder is often used as bleaching agent. It works because of oxidation. Chlorine in the bleaching powder is responsible for bleaching effect.
Use of Bleaching Powder:
- Bleaching powder is used as disinfectant to clean water, moss remover, weed killers, etc.
- Bleaching powder is used for bleaching of cotton in textile industry, bleaching of wood pulp in paper industry.
- Bleaching powder is used as oxidizing agent in many industries, such as textiles industry, paper industry, etc.
3. Baking Soda (NaHCO3): Baking soda is another important product which can be obtained using byproducts of chlor – alkali process. The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) or sodium bicarbonate. Bread soda, cooking soda, bicarbonate of soda, sodium bicarb, bicarb of soda or simply bicarb, etc. are some other names of baking soda.
Preparation Method: Baking soda is obtained by the reaction of brine with carbon dioxide and ammonia. This is known as Solvay process.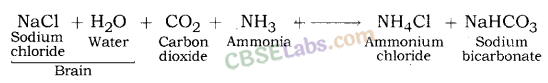
In this process, calcium carbonate is used as the source of CO2 and the resultant calcium oxide is used to recover ammonia from ammonium chloride.
Properties of Sodium Bicarbonate:
- Sodium bicarbonate is white crystalline solid, but it appears as fine powder.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate is amphoteric in nature.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate is sparingly soluble in water.
- Thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda).
- When baking soda is heated, it decomposes into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide and water.
2NaHCO3 + heat → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O - Sodium carbonate formed after thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide on further heating.
Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
This reaction is known as Dehydration reaction.
Use of Baking Soda:
- Baking soda is used in making of baking powder, which is used in cooking as it produces carbon dioxide which makes the batter soft and spongy.
- Baking soda is used as an antacid.
- Baking soda is used in toothpaste which makes the teeth white and plaque free.
- Baking soda is used in cleansing of ornaments made of silver.
- Since sodium hydrogen carbonate gives carbon dioxide and sodium oxide on strong heating, thus, it, is used as a fire extinguisher.
Baking Powder: Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces carbon dioxide on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. The sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter.
Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder.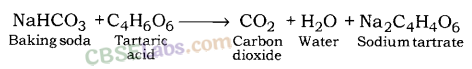
When baking powder is heated, sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) decomposes to give CO2 and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). CO2 causes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of Na2CO3.
4. Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate)
Preparation Method: Sodium carbonate is manufactured by the thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate obtained by Solvay process.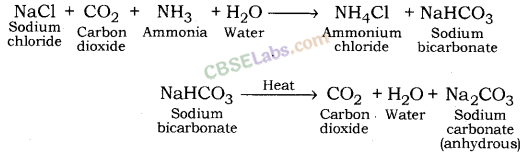
The sodium carbonate obtained in this process is dry. It is called Soda ash or Anhydrous sodium carbonate. Washing soda is obtained by rehydration of anhydrous sodium carbonate.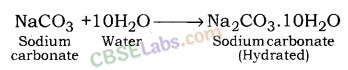
Since there are 10 water molecules in washing soda, hence, it is known as Sodium Bicarbonate Decahydrate.
Sodium carbonate is a crystalline solid and it is soluble in water when most of the carbonates are insoluble in water.
Use of sodium carbonate:
- It is used in the cleaning of cloths, especially in rural areas.
- In the making of detergent cake and powder.
- In removing the permanent hardness of water.
- It is used in glass and paper industries.
The water of Crystallization: Many salts contain water molecule and are known as Hydrated Salts. The water molecule present in salt is known as Water of crystallization.
Examples:
Copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O): Blue colour of copper sulphate is due to presence of 5 molecules of water. When copper sulphate is heated, it loses water molecules and turns: into grey – white colour, which is known as anhydrous copper sulphate. After adding water, anhydrous copper sulphate becomes blue again.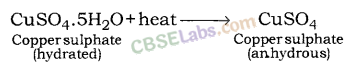
Reactions Of Important Chemical Compounds:
- Preparation of Bleaching powder: By the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O - On heating, baking soda liberates CO2
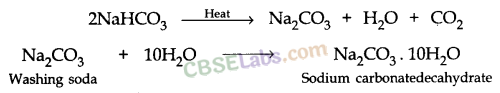
- Preparation of Plaster of Paris:
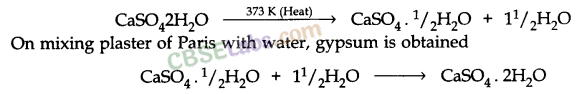
Metals: Physical properties of metals, chemical properties of metals and non-metal oxide.
Metals are the elements that conduct heat and electricity and are malleable and ductile. Examples are Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Platinum (Pt), Lead (Pb), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) etc.
Metals are the elements which form positive ions by losing electrons. Thus, metals are known as Electropositive Elements.
Physical Properties of Metals
- Hardness: Most of the metals are hard, except alkali metals, such as sodium, potassium, lithium, etc. are very soft metals. These can be cut by using a knife.
- Strength: Most of the metals are strong and have high tensile strength. Because of this, big structures are made using metals, such as copper (Cu) and iron (Fe). (Except Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) which are soft metals).
- State: Metals are solid at room temperature except for mercury (Hg).
- Sound: Metals produce ringing sound, so, metals are called Sonorous. Sound of metals is also known as Metallic sound. This is the cause that metal wires are used in making musical instruments.
- Conduction: Metals are a good conductor of heat and electricity. This is the cause that electric wires are made of metals like copper and aluminium.
- Malleability: Metals are malleable. This means metals can be beaten into a thin sheet. Because of this property, iron is used in making big ships.
- Ductility: Metals are ductile. This means metals can be drawn into thin wire. Because of this property, a wire is made of metals.
- Melting and Boiling Point: Metals have generally high melting and boiling points.
1. Reaction with oxygen: Most of the metals form respective metal oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Examples:
Reaction of Potassium with Oxygen: Potassium metal forms potassium oxide when reacts with oxygen.
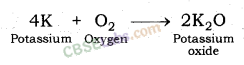
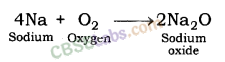
Reaction of Copper metal with Oxygen: Copper does not react with oxygen at room temperature but when burnt in air, it gives oxide.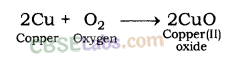
Silver, gold and platinum do not combine with the oxygen of air even at high temperature. They are the least reactive.
2. Reaction of metals with water: Metals form respective hydroxide and hydrogen gas when reacting with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
Most of the metals do not react with water.
Reaction of Sodium metal with Water: Sodium metal forms sodium hydroxide and liberates hydrogen gas along with lot of heat when reacting with water.
Reaction of Calcium metal with Water: Calcium forms calcium hydroxide along with hydrogen gas and heat when react with water.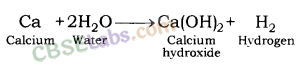
Reaction of Magnesium metal with Water: Magnesium metal reacts with water slowly and forms magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.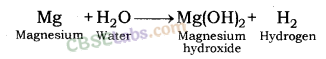
When steam is passed over magnesium metal, magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas are formed.
Reactivity Series of Metals: The order of intensity or reactivity of metal is known as Reactivity Series. Reactivity of elements decreases on moving from top to bottom in the given reactivity series.
In the reactivity series, copper, gold, and silver are at the bottom and hence, least reactive. These metals are known as Noble metals. Potassium is at the top of the series and hence, most reactive.
Reactivity of some metals are given in descending order :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts: Reaction of metals with the solution of other metal salt is displacement reaction. In this reaction, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt.
Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Examples :
Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.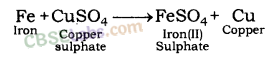
Similarly, aluminium and zinc displace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.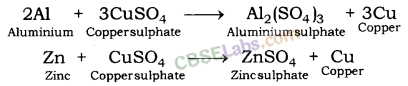
In all the above examples, iron, aluminium and zinc are more reactive than copper. This is why they displace copper from its salt solution.
When copper is dipped in the solution of silver nitrate, it displaces silver and forms copper nitrate.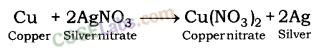
In the reaction, copper is more reactive than silver and hence, displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
Silver metal does not react with copper sulphate solution because silver is less reactive than copper and not able to displace copper from its salt solution.
Similarly, when gold is dipped in the solution of copper nitrate, no reaction takes place because copper is more reactive than gold.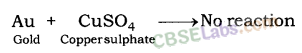
Non-Metals: Physical Properties of non-metals, chemical properties of non-metals, non¬metal oxides, Reaction of metal and Non-metal, Ionic bonds and formation of an ionic bond. Non-metals are the elements that do not conduct electricity and are neither malleable nor ductile.
Examples: Carbon (C), Sulphur (S), Phosphorous (P), Silicon (Si), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Neon (Ne) and Argon (Ar) etc.
Non-metals are the elements which form negative ions by gaining an electron. Thus, non¬metals are also known as Electronegative Elements.
Physical properties of non-metals
- Hardness: Non-metals are not hard rather they are generally soft. But the diamond is an exception; it is the hardest naturally occurring substance.
- State: Non-metals may be solid, liquid or gas.
- Lustre: Non-metals have a dull appearance. Diamond and iodine are exceptions.
- Sonority: Non-metals are not sonorous, i.e., they do not produce a typical sound on being hit.
- Conduction: Non-metals are a bad conductor of heat and electricity. Graphite which is allotrope of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exception.
- Malleability and ductility: Non-metals are brittle.
- Melting and boiling point: Non-metals have generally low melting and boiling points.
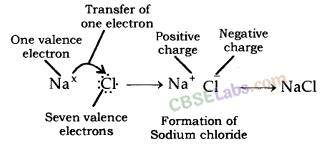
Atomic number of sodium = 11
Electronic configuration of sodium : 2, 8, 1
Number of electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Valence electrons = Electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Atomic number of chlorine = 17
Electronic configuration of chlorine : 2, 8, 7
Electrons in outermost orbit = 7
Therefore, valence electrons = ?
Properties of Ionic compound
- Ionic compounds are solid. Ionic bond has a greater force of attraction because of which ions attract each other strongly. This makes ionic compounds solid.
- Ionic compounds are brittle.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because force of attraction between ions of ionic compounds is very strong.
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve in water.
- Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in organic solvents; like kerosene, petrol, etc.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals: Minerals, ores, extraction of metals of least reactivity, extraction of metals of middle reactivity, extraction of metals of high reactivity, refining or purification of metals and corrosion.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals:
Source of metal: Metals occur in Earth’s crust and in seawater; in the form of ores. Earth’s crust is the major source of metal. Seawater contains many salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc
Mineral: Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have a uniform composition.
Ores: The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called Ores.
Metals found at the bottom of reactivity series are least reactive and they are often found in nature in free-state; such as gold, silver, copper, etc.
Metals found in the middle of reactivity series, such as Zn, Fe, Pb, etc. are usually found in the form of oxides, sulphides or carbonates.
Metals found at the top of the reactivity series are never found in free-state as they are very reactive, example; K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al, etc.
Many metals are found in the form of oxides because oxygen is abundant in nature and is very reactive.
Extraction of Metals: Metals can be categorised into three parts on the basis of their reactivity: Most reactive, medium reactive and least reactive.
1. Concentration of Ores: Removal of impurities, such as soil, sand, stone, silicates, etc. from mines ore is known as Concentration of Ores.Ores which are mined often contain many impurities. These impurities are called gangue. First of all, concentration is done to remove impurities from ores. The concentration of ores is also known as enrichment of ores. Process of concentration depends upon physical and chemical properties of ores. Gravity separation, electromagnetic separation, froth flotation process, etc. are some examples of the processes which are applied for concentration of ores.
2. Conversion of Concentrated Ore into Crude Metal
Conversion of metals ores into oxides: It is easy to obtain metals from their oxides. So, ores found in the form of sulphide and carbonates are first converted to their oxides by the process of roasting and calcination. Oxides of metals so obtained are converted into metals by the process of reduction.
Roasting: Heating of sulphide ores in the presence of excess air to convert them into oxides is known as Roasting.![]()
Calcination: Heating of carbonate ores in the limited supply of air to convert them into oxides is known as Calcination.
(i) Extraction of Metals of Least Reactivity: Mercury and copper, which belong to the least reactivity series, are often found in the form of their sulphide ores. Cinnabar (HgS) is the ore of mercury. Copper glance (Cu2S) is the ore of copper.
Extraction of Mercury Metal: Cinnabar (HgS) is first heated in air. This turns HgS (mercury sulphide or cinnabar) into HgO (mercury oxide) by liberation of sulphur dioxide. Mercury oxide so obtained is again heated strongly. This reduces mercury oxide to mercury metal.
Extraction of Copper Metal: Copper glance (Cu2S) is roasted in the presence of air. Roasting turns copper glance (ore of copper) into copper (l) oxide. Copper oxide is then heated in the absence of air. This reduces copper (l) oxide into copper metal.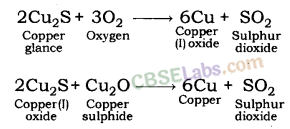
(ii) Extraction of Metals of Middle Reactivity: Iron, zinc, lead, etc. are found in the form of carbonate or sulphide ores. Carbonate or sulphide ores of metals are first converted into respective oxides and then oxides are reduced to respective metals.
Extraction of Zinc: Zinc blende (ZnS: zinc sulphide) and smithsonite or zinc spar or calamine (ZnCO3: zinc carbonate) are ores of zinc. Zinc blende is roasted to be converted into zinc oxide. Zinc spar is put under calcination to be converted into zinc oxide.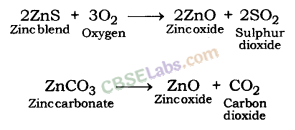
Zinc oxide so obtained is reduced to zinc metal by heating with carbon (a reducing agent).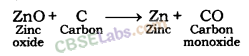
Extraction of Iron from Haematite (Fe2O3): Haematite ore is heated with carbon to be reduced to iron metal.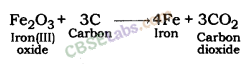
Extraction of Lead from Lead oxide: Lead oxide is heated with carbon to be reduced to lead metal.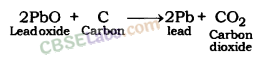
Reduction of Metal oxide by Heating with Aluminium: Metal oxides are heated with aluminium (a reducing agent) to be reduced to metal. Following is an example: Manganese dioxide and copper oxide are reduced to respective metals when heated with aluminium.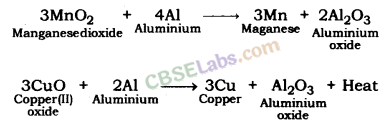
Thermite Reaction: Ferric oxide; when heated with aluminium; is reduced to iron metal. In this reaction, a lot of heat is produced. The thermite reaction is used in the welding of electric conductors, iron joints, etc. such as joints in railway tracks. This is also known as Thermite Welding (TW).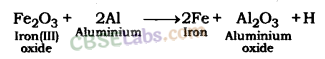
(iii) Extraction of Metals of High Reactivity: Metals of high reactivity; such as sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, etc. are extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction. These metals cannot be reduced using carbon because carbon is less reactive than them.
Electrolytic Reduction: Electric current is passed through the molten state of metal ores. Metal being positively charged is deposited over the cathode.
Example: When an electric current is passed through molten state or solution of sodium chloride, sodium metal gets deposited over the cathode.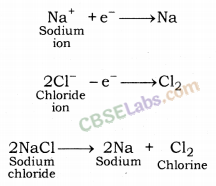
4. Refining or purification of metals: Metals extracted from various methods contains some impurities, thus, they are required to be refined. Most of the metals are refined using electrolytic refining.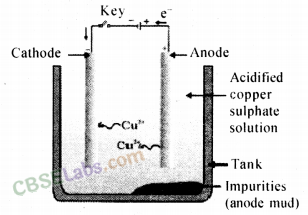
Electrolytic Refining: In the process of electrolytic refining, a lump of impure metal and a thin strip of pure metal are dipped in the salt solution of metal to be refined. When an electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal is deposited over a thin strip of pure metal
from a lump of impure metal. In this, impure metal is used as anode and pure metal is used as a cathode.
Electrolytic Refining of Copper: A lump of impure copper metal and a thin strip of pure copper are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate. Impure lump of metal is connected with the positive pole and thin strip of pure metal is connected with negative pole. When electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal from anode moves towards cathode and is deposited over it. Impurities present in metal are settled near the bottom of anode in the solution. Settled impurities in the solution are called Anode Mud.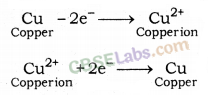
5. Corrosion: Most of the metals keep on reacting with the atmospheric air. This leads to the formation of a layer over the metal. In the long run, the underlying layer of metal keeps on getting lost due to conversion into oxides or sulphides or carbonate, etc. As a result, the metal gets eaten up. The process is called Corrosion.
Rusting of Iron: Rusting of iron is the most common form of corrosion. When iron articles like the gate, grill, fencing, etc. come in contact with moisture present in the air, the upper layer of iron turns into iron oxide. Iron oxide is brown-red in colour and is known as Rust. The phenomenon is called Rusting of Iron.
If rusting is not prevented in time, the whole iron article would turn into iron oxide. This is also known as Corrosion of Iron. Rusting of iron gives a huge loss every year.
Prevention of Rusting: For rusting, iron must come in contact with oxygen and water. Rusting is prevented by preventing the reaction between atmospheric moisture and the iron article. This can be done by:
- Painting
- Greasing
- Galvanization
- Electroplating
- Alloying
6. Alloys: The homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal is called Alloy.
Types of alloys :
- Ferrous alloys: An alloy in which iron (Fe) is present. For example : manganese steel (Fe = 86% ; Mn = 13% ; C = 1%) and Nickle steel (Fe = 98% ; Ni = 2%).
- Non-ferrous alloys: An alloy does not contain iron. For example : Brass (Cu = 80% ; Zn = 20%), and Bronze (Cu = 90% ; Sn = 10%).
- Amalgams: An alloy in which mercury (Hg) is present. For example Sodium amalgams [Na(Hg)] and Zinc amalgams [Zn(Hg)]
- Alloys are stronger than the metal from which they are obtained.
- It is harder than the constituent metals.
- More resistance to corrosion.
- The melting point of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
Example: Solder [Sn(80%) + Pb(50%)] has lower m. p. than Pb and Sn. - The electrical conductivity of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
CHAPTER 4
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
Bonding in Carbon: The Covalent bond, Electron dot structure, Physical properties of organic compounds, Allotropes of Carbon.
Covalent Bond: The atomic number of carbon is 6. Its electronic configuration is 2, 4. It requires, 4 electrons to achieve the inert gas electronic configuration. But carbon cannot form an ionic bond.
It could gain four electrons forming C4- cation. But it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
It could lose four electrons forming C4+ cations. But it requires a large amount of energy to remove four electrons.
Thus, carbon overcomes this problem by sharing of its valence electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements.
The bond formed by mutual sharing of electron pairs between two atoms in a molecule is known as Covalent Bond.
Types of Covalent Bond:
- Single Covalent Bond: When a single pair of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; F2, Cl2, H2 etc.
- Double Covalent Bond: When two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; O2, CO2 etc.
- Triple Covalent Bond: When three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; N2 etc.
Electron Dot Structure: The electron dot structures provides a picture of bonding in molecules in terms of the shared pairs of electrons and octet rule.
Formation of Hydrogen Molecule
Atomic number of Hydrogen = 1
Number of valence electrons = 1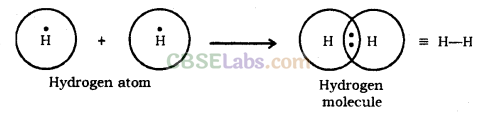
Formation of CH4 Molecule
Atomic number of Carbon = 6 [2, 4]
Number of valence electrons = 4
Atomic number of Hydrogen = 1
Number of valence electrons = 1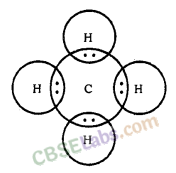
Formation of CO2 Molecule
Atomic number of Carbon = 6 [2, 4]
Number of valence electrons = 4
Atomic number of Oxygen = 8 [2, 6]
Number of valence electrons = 6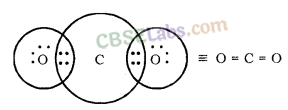
Formation of H2S Molecule
Atomic number of Sulphur = 16 [2, 8, 6]
Number of valence electrons = 6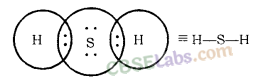
Physical Properties of Organic Compounds
Most of the organic compounds have low boiling and melting point, due to the weak force of attraction (i.e., the inter-molecular force of attraction) between these molecules.
Most carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity, due to the absence of free electrons and free ions.
Allotropes of Carbon
Allotropy: The phenomenon in which the element exists in two or more different physical states with similar chemical properties are called Allotropy.
Carbon has Three Main Allotropes
- Diamond: In this, carbon, an atom is bonded to four other atoms of carbon forming three-dimensional structures. It is the hardest substance and an insulator. It is used for drilling rocks and cutting. It is also used for making jewellery.
- Graphite: In this, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. It is a good conductor of electricity and used as a lubricant.
- Buckminster Fullerene: It is an allotrope of the carbon-containing cluster of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules. It is dark solid at room temperature.
Versatile nature of Carbon, Hydrocarbons, Isomerism, Homologous series, Functional groups, Nomenclature of functional groups.
Versatile Nature of Carbon: The existence of such a large number of organic compounds is due to the following nature of carbon,
- Catenation
- Tetravalent nature.
(i) Catenation: The self linking property of an element mainly carbon atom through covalent bonds to form long straight, branched and rings of different sizes are called Catenation.
This property is due to
- The small size of the carbon atom.
- The great strength of the carbon-carbon bond.
Carbon can also form stable multiple bonds (double or triple) with itself and with the atoms of other elements.
Straight Chain
Branched Chain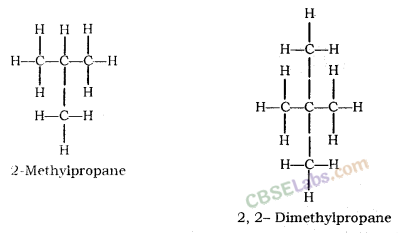
Rings
(ii) Tetravalent Nature: Carbon has valency of four. It is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or some other heteroatoms with single covalent bond as well as double or triple bond.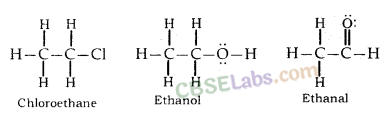
Hydrocarbons: Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons.
For example; Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Ethene (C2H4), Ethyne (C2H2) etc.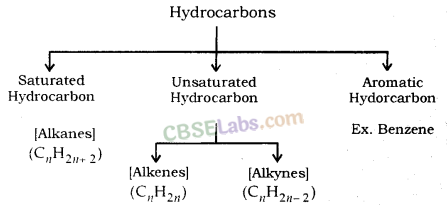
Saturated Hydrocarbon (Alkanes): General formula is CnH2n+2.
n = number of carbon atoms.
In this, the carbon atoms are connected by only a single bond.
For example; Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6) etc.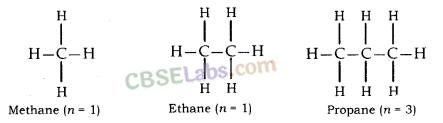
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Alkenes: General formula is CnH2n, where n = number of carbon atoms.
In this, the two carbon atoms are connected by double bond.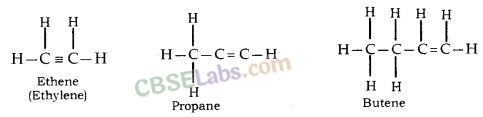
Alkynes: General formula is CnH2n-2, where n = number of carbon atoms. In this, the two carbon atoms are connected by triple bond.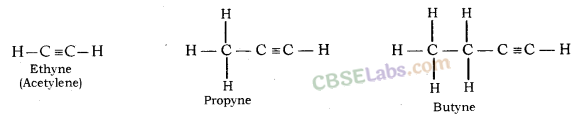
Electron Dot Structure of Hydrocarbons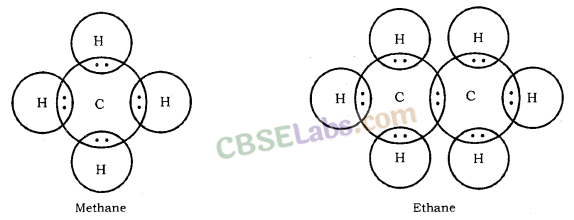
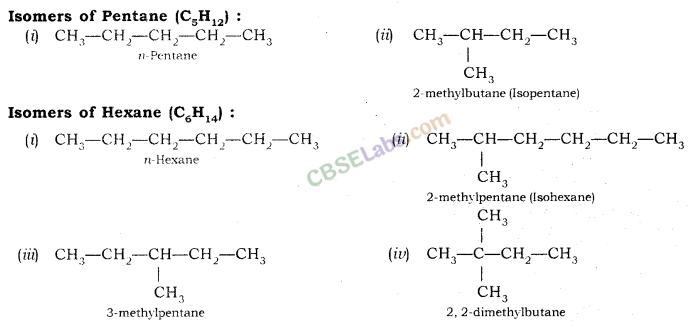
Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formula and properties are known as Isomers and this phenomenon is known as Isomerism.
Structural Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are called Structural isomers. Example: Isomers of butane (C4H10)
Homologous Series: Series of organic compounds having the same functional group and chemical properties and successive members differ by a CH2 unit or 14 mass units are known as Homologous series.
Homologous series of Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes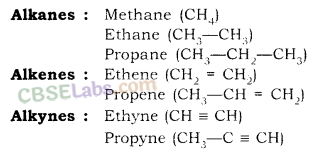
Characteristic of Homologous Series
- The successive members in homologous series differ by CH2 unit or 14 mass unit.
- Members of given homologous series have the same functional group.
- All the members of homologous series shows similar chemical properties.
Functional Group: An atom or group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties are called Functional Group.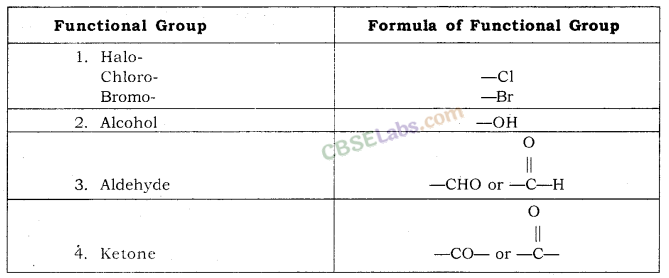
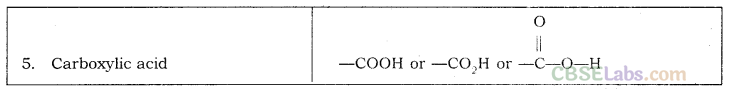
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds: It is difficult to remember millions of compounds by their individual common name. Thus, to systematize the nomenclature of organic compounds IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) has given certain rule which is as follows:
1. Identify the Number of Carbon Atoms in the Compound
| S. No | Number of Carbon Atoms | Word Root (-) (Suffix) | Single bond |
| 1. | One carbon atoms (1-C) | Meth | + ane |
| 2. | Two carbon atoms (2-C) | Eth | + ane |
| 3. | Three carbon atoms (3-C) | Prop | + ane |
| 4. | Four carbon atoms (4-C) | But | + ane |
| 5. | Five carbon atoms (5-C) | Pent | + ane |
| 6. | Six carbon atoms (6-C) | Hex | + ane |
2. Identify the functional group
| S. No. | Functional Group | Prefix | Suffix |
| 1. | Double bond (=) | — | ene |
| 2. | Triple bond (≡) | — | yne |
| 3. | Chlorine (—Cl) | Chloro | — |
| 4. | Bromine (—Br) | Bromo | — |
| 5. | Alcohol (-OH) | — | ol |
| 6. | Aldehyde (-CHO) | — | al |
| 7. | Ketone (-CO-) | — | one |
| 8. | Carboxylic acid (-COOH) | — | oic acid |
3. Name the Compounds By Following Order
Prefix + Word Root + Suffix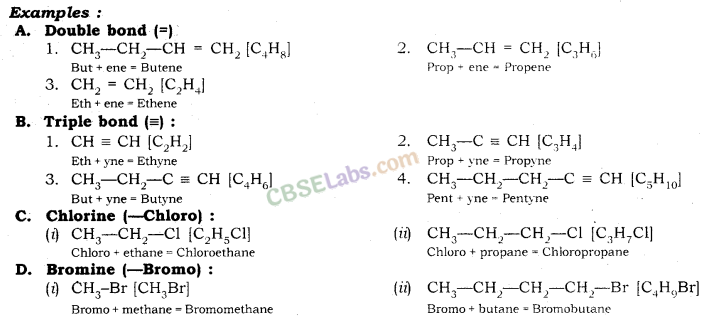
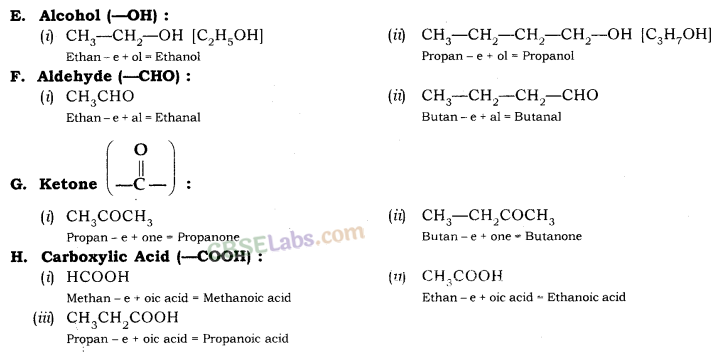
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds: The important chemical properties are as follows:
1. Combustion: The complete combustion of carbon compounds in the air gives carbon dioxide water, heat and light.
CH3CH2OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + Heat and light
Carbon burns in air or oxygen to give carbon dioxide and heat and light.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat and light
Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a blue flame in the presence of a sufficient supply of air or oxygen.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + Heat and light
In presence of limited supply of air, saturated hydrocarbon forms a sooty flame.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons burn with a yellow smoky flame.
The gas and kerosene stove used at home has inlet for air so that, burnt to given clean blue flame.
Due to presence of small amount of nitrogen and sulphur, coal and petroleum produces carbon dioxide with oxides of nitrogen and sulphur which are major pollutant.
2. Oxidation: Oxidation of ethanol in presence of oxidizing agents gives ethanoic acid.
Oxidizing Agent: Some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others, are known as Oxidising Agent.
Example: Alkaline KMnO4 (or KMnO4—KOH)
Acidified K2Cr2O7 (or K2Cr2O7—H2SO4)
KMnO4 – Potassium permanganate
K2Cr2O7 – Potassium dichromate
3. Addition Reaction: Addition of dihydrogen with unsaturated hydrocarbon in the presence of catalysts such as nickel or platinum or palladium are known as Hydrogenation (addition) reaction.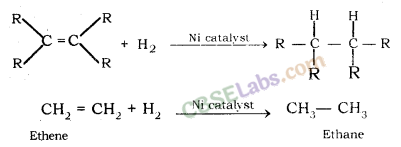
Catalyst: Substances that cause a reaction to occur or proceeds to different rate without consuming in it are called a catalyst. For example; Ni, Pt, Pd, etc.
Process of converting vegetable oil into solid fat (vegetable ghee) is called Hydrogenation of Oil.
Vegetable oil + H2
Vegetable fats are saturated fats which are harmful for health.
Vegetable oil containing unsaturated fatty acids are good for health.
4. Substitution Reaction: Replacement of one or more hydrogen atom of an organic molecule by another atom or group of the atom is known as Substitution Reaction.
Some Important Carbon Compounds :
Ethanol (CH3CH2—OH): Commonly known as Ethyl Alcohol.
Physical Properties
- It is colourless, inflammable liquid.
- It is miscible with water in all proportions.
- It has no effect on the litmus paper.
Chemical Properties
- Reaction with sodium

- Reaction with concentrated H2SO4 (Dehydration Reaction)
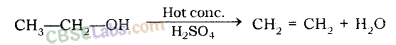
Dehydrating agent: Substances which removes water from ethanol (alcohols) is known as Dehydrating agent. For example; Cone. H2SO4.
Uses: As solvent, as antiseptic (tincture iodine), as anti-freeze in automobiles.
Ethanoic Acid (CH3COOH): Commonly known as Acetic acid. 5-8% of ethanoic acid in water is called Vinegar. The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence, it often freezes in cold climate so named as glacial acetic acid.
Physical Properties
- It is a colourless, pungent-smelling liquid.
- Miscible with water in all proportions.
- Turns blue litmus to red.
Chemical Properties
(i) Esterification Reaction: Reaction of ethanoic acid with an alcohol in the presence of a few drops of conc. H2SO4 as catalyst gives a sweet-smelling substance known as Esters, called Esterification reaction.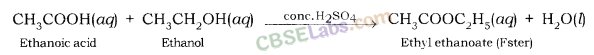
Esters are used in making perfumes and flavouring agents.
Saponification Reaction: Reaction of esters with sodium hydroxide, gives alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid (soap). This reaction is known as Saponification Reaction.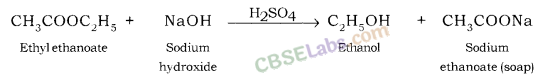
(ii) Reaction with Carbonates and Hydrogen Carbonates: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonates and sodium hydrogen carbonates to give rise to a salt, carbon dioxide and water.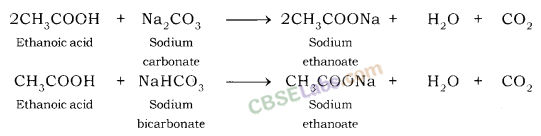
- Used as vinegar.
- Used as raw material for the preparation of acetyl chloride and esters.
Soap: Sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids is called Soap.
General formula: RCOO–Na+
Detergent: Ammonium and sulphonate salts of long chain fatty acids are called Detergent.
Example: CH3—(CH2)11—C6H4—SO3Na.
Hard and Soft Water: Water that does not produce lather with soap readily is called Hard water and which produces lather with soap is called Soft Water.
Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, chlorides and sulphate salt of calcium and magnesium.
Difference between soaps and detergents
| Soaps | Detergents |
| (i) These are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids. | (i) These are ammonium and sulphonate salts of long chain fatty acids. |
| (ii) Ionic part of the soap is —COO–Na+ | (ii) Ionic part of detergent is —OSO3-Na+. |
| (iii) Their efficiency decreases in hard water | (iii) Their efficiency is unaffected in hard water. |
| (iv) Soaps are biodegradable. | (iv) Detergents are non-biodegradable. |
Advantage of Detergents: The main advantage of detergent over soaps is that soaps cannot be used in hard water for washing because hard water reacts with soap to form curdy white precipitate called Scum.
Thus, in hard water, soap does not give lather while detergent does.
Cleansing Action of Soaps and Detergents: Both soaps and detergents cantains two parts. A long hydrocarbon part which is hydrophobic (water repelling) in nature and a short ionic part which is hydrophillic (water attracting) in nature.
The hydrocarbon part of the soap molecule links itself to the oily (dirt) drop and ionic end orients itself towards water and forms a spherical structure called micelles. The soap micelles helps in dissolving the dirt in water and wash our clothes.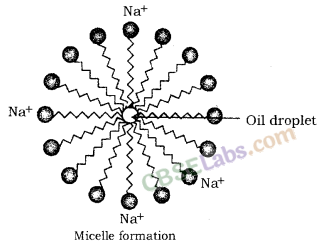
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment